Ban on Chinese connected-car software is almost ready
NatSec reasons
Ban on Chinese connected-car software is almost ready
There are some exemptions, but the rule would block imports from MY2027.
28
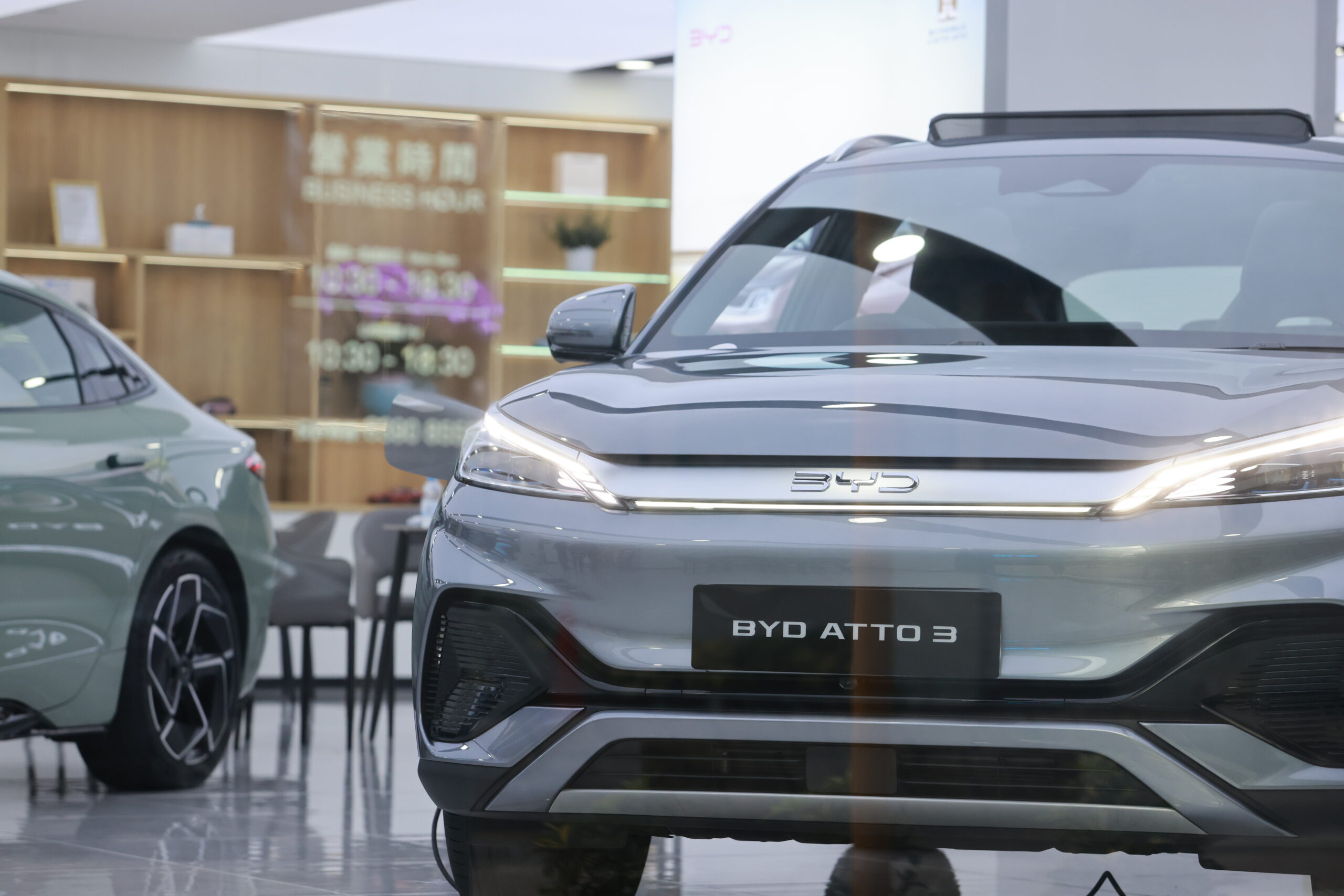 Chinese brand BYD will have an even harder time trying to enter the US as a result of the new rule banning Chinese connected vehicle systems.
Chinese brand BYD will have an even harder time trying to enter the US as a result of the new rule banning Chinese connected vehicle systems.
Credit:
Getty Images
Chinese brand BYD will have an even harder time trying to enter the US as a result of the new rule banning Chinese connected vehicle systems.
Credit:
Getty Images
Text settings
Story text
Size
Small Standard Large
Width *
Standard Wide
Links
Standard Orange
* Subscribers only
Learn more
Minimize to nav
Plans to block new vehicles with software and hardware linked to either China or Russia are moving ahead. Today, the Department of Commerce published a final rule in the Federal Register that will prohibit the import of vehicles with Chinese or Russian connected-car vehicle software from model year 2027 and Chinese or Russian hardware from model year 2030.
While the move will no doubt protect domestic auto manufacturing from the threat of cheap imports, the ban has been proposed on national security grounds. Specifically, the US government has determined that "malign actors and foreign adversaries" could exploit the "progressively more complex hardware and software systems" on new cars. It also determined that the danger of that happening when that software or hardware is made by a company owned or controlled by either China or Russia is unacceptably high.
The proposed rule covers hardware and software that enable connectivity above 450 MHz and automated driving system software—the sensors or other ADS hardware is not covered by the rule. Originally, the government had also wanted to include OSes, telematics, battery management systems, and advanced driver assistance systems but narrowed the scope in response to public comments. (It also notes that while telematics are indeed a prime attack surface for a foreign adversary since they operate over cellular protocols, that's already covered.)
However, the ban, as written, is not absolute. Companies can seek authorization to import software or hardware that would otherwise be outlawed, but the request would need to satisfy the US government and possibly be subject to conditions.
There are also exemptions for software for vehicles older than model year 2027 and hardware for vehicles older than model year 2030, including parts imported for warranty or repair work. (The government points out that retroactively applying the new rule would be a little pointless as any harm would already be done by vehicles that had compromised systems that predate it going into effect.)
And the final rule would only apply to light-duty vehicles. Anything with a gross vehicle weight rating of more than 10,000 lbs is exempt but will be dealt with in "a separate regulation tailored to the commercial sector in the coming months."
Auto industry suppliers probably face the most disruption as a result of the new rule—just the presence of a Chinese-made module in a larger system is enough to trigger the import ban. But there should be little disruption to the US car market, at least for now.
Since the rules only go into effect from model year 2027, the few Chinese-made vehicles on sale in the US—models from Polestar, Volvo, Lincoln, and Buick—may remain on sale. However, Polestar's Chinese ownership may prove somewhat of a sticking point compared to Ford and GM. Ars notes that lawyers representing Polestar met with the Commerce Department last week—we reached out to the automaker for a comment and will update this piece should we hear back.


















Comments
0 comment