Last Updated:
Untreated earwax build-up can block the ear canal and may cause hearing loss. Dr Manish Munjal of Delhi’s Sir Ganga Ram Hospital shares simple tips on how to remove it safely

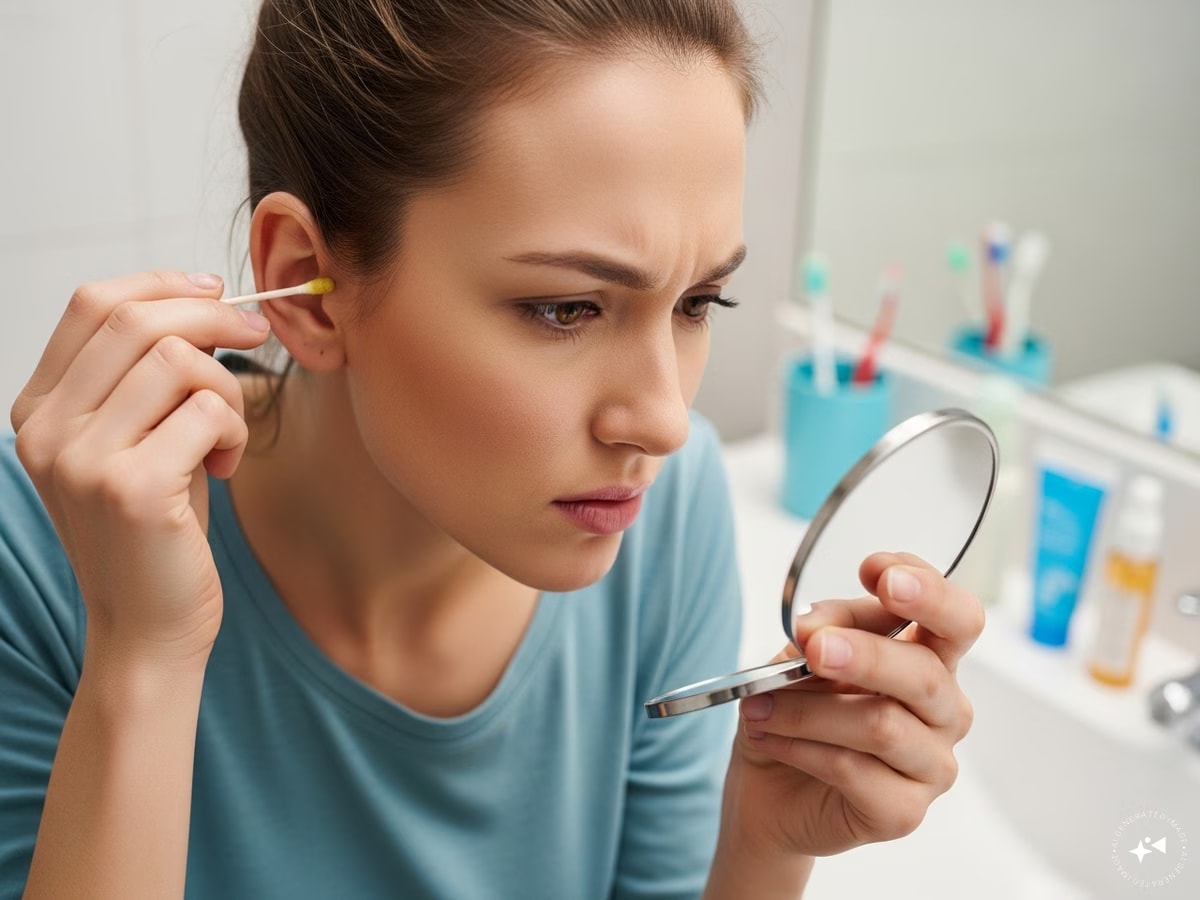
If earwax hardens and is left untreated, it can cause pain, itching, or even a tingling sensation in the ear. (AI Generated)
Earwax, known medically as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the ear to clean and protect itself. However, when it hardens, it can cause pain, itching, or even a tingling sound in the ear.
In severe cases, untreated earwax build-up, also called cerumen impaction, can block the ear canal and lead to hearing loss. To understand safe ways of managing this common issue, the News18 team reached out to Dr Manish Munjal, Vice Chairperson of the ENT Department at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, Delhi, who shared simple and effective methods to remove hardened earwax.
Recommended Stories
Dr Munjal emphasised that one should never insert cotton buds, matchsticks, or any sharp objects into the ear as these can push the wax deeper or cause permanent ear damage. Instead, he suggested safer alternatives mentioned below:
Ear drops
The first step is to soften the hardened earwax. Over-the-counter ear drops are easily available at chemist shops and do not require a prescription. By applying these drops regularly for three days, the wax usually softens and comes out naturally. If the blockage persists, a doctor can quickly remove it using a microscopic clearance technique.
Baby oil or Mineral Oil
If ear drops are not available, baby oil or mineral oil can also be used. Applied in the same way, they help soften the wax within three days. However, Dr Munjal warned against using other oils or inserting foreign objects in the ear.
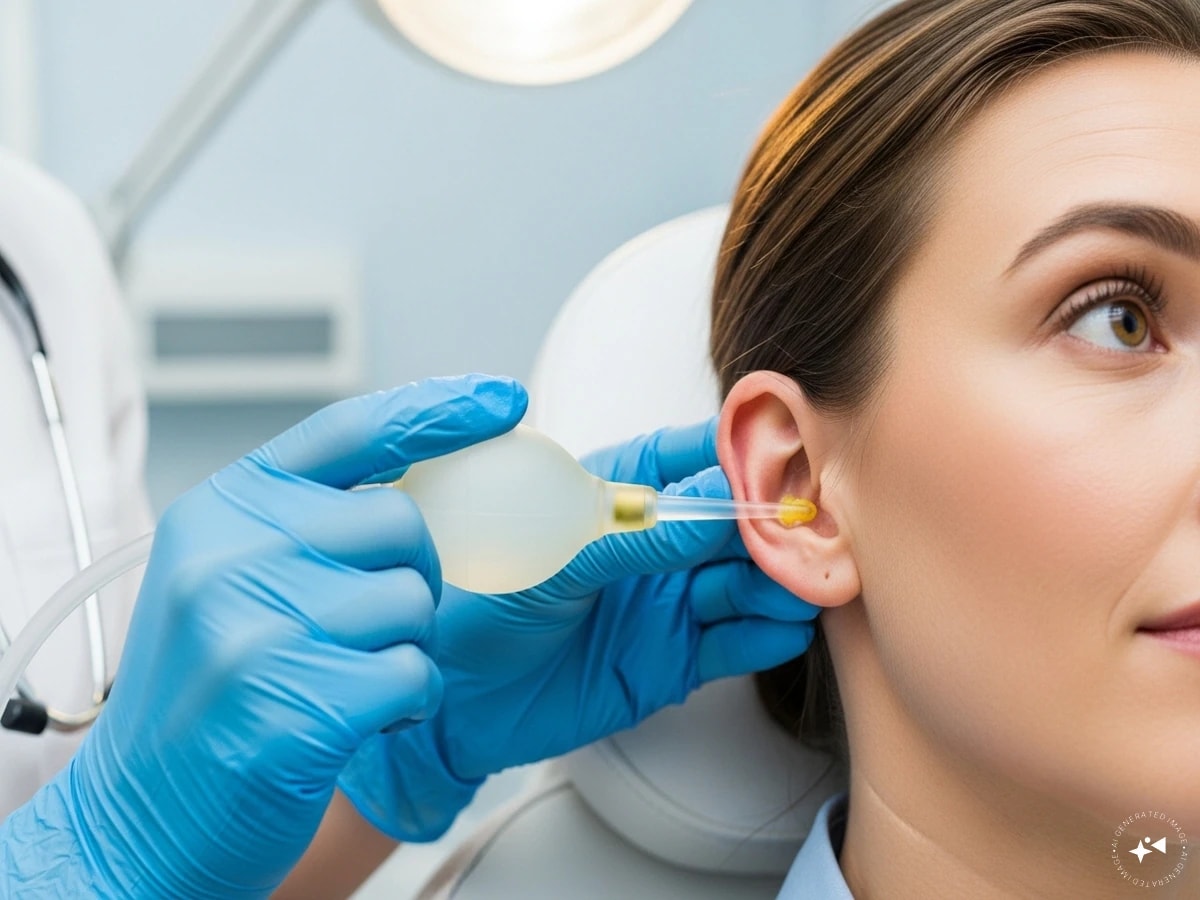
Suction Bulb
A suction bulb, priced between Rs 300 and Rs 1,500, is available in chemist shops and online. Working on pressure technology, it pulls out earwax by creating gentle suction. This simple method usually clears the ear within a minute or two.
Ear Irrigation
If ear drops fail, ear irrigation is another option. This should only be performed by a trained expert. In this procedure, a saline solution is filled into the ear with a syringe and gently flushed out using a microscopic bulb syringe, which removes the wax safely.
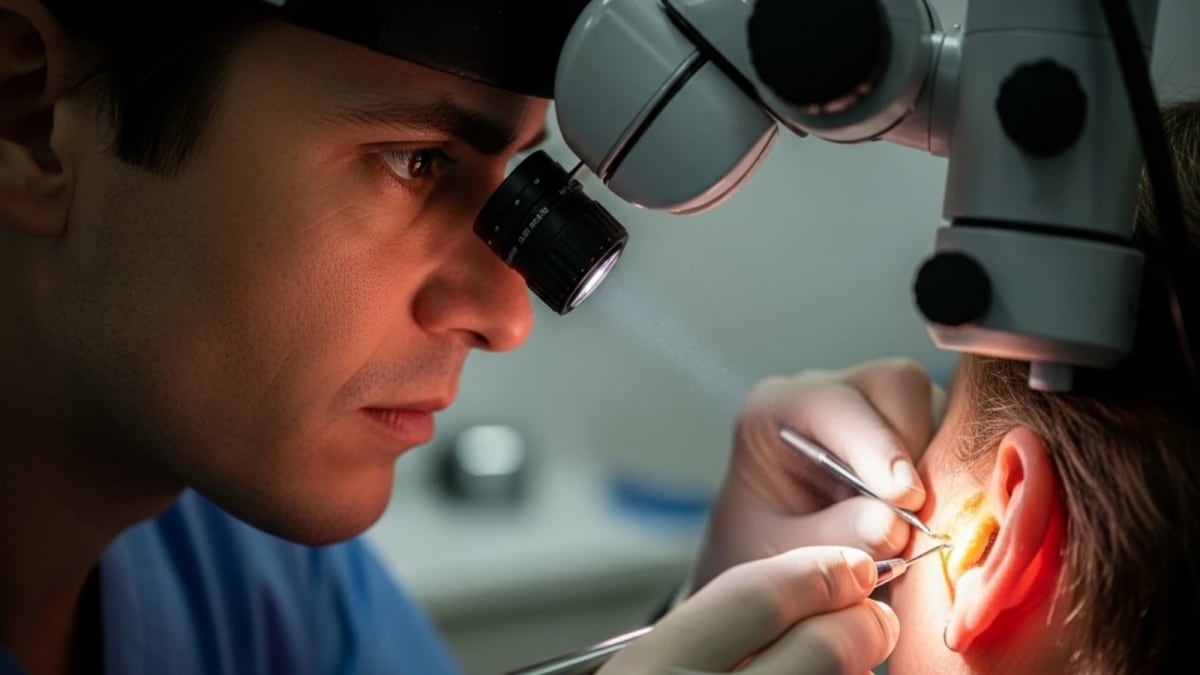
Ear Microscopy (Otoscopy)
In cases of severe blockage where the wax has hardened, doctors use an ear microscope. A telescope is inserted into the ear, and under direct vision, the wax is carefully removed with specialised instruments. This safe and precise technique is commonly used in hospitals.
Dr Munjal advised that while home remedies can help in mild cases, professional intervention is important if discomfort continues. Left untreated, hard earwax can lead to serious complications, including long-term hearing loss.
Loading comments…
Go to Source
Author: News18