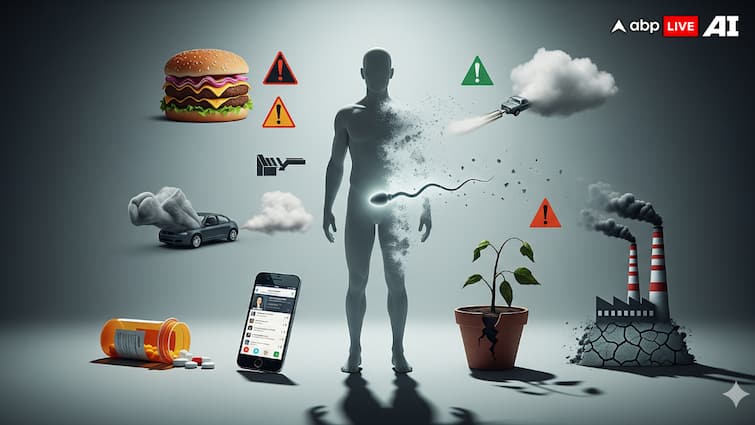
A comprehensive global meta-analysis, published by the Oxford University Press in its Human Reproduction Update, 2017, found a 50–60% drop in sperm count between 1973 and 2011 among men in North America, Europe, Australia, and New Zealand. This decline — about 1.4% per year — was seen across both fertile and general populations.
India, too, has not been spared. A study published by the Male Reproductive Biology Laboratory, Lucknow, published in Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology (2018), showed a significant deterioration in semen quality among Indian men over a 37-year period.
Why Experts Are Concerned
Recent coverage in The Guardian highlights that sperm counts globally have been declining at an even faster pace since 2000 — over 2% annually. Scientists point to environmental toxins such as phthalates and bisphenols, commonly found in plastics, which can disrupt hormones and reproductive health.
“Fertility issues have long been seen as a woman’s problem, but in reality, male factors are responsible for almost half of all infertility cases worldwide,” says Dr. Nishi Singh, Head, Prime IVF.
She adds that despite scientific evidence, myths and misconceptions about male fertility still thrive—causing confusion, stigma, and stress among men.
Myths vs Facts About Male Fertility
Myth 1: Male fertility declines only after 50
“Although men can father children even at later ages, sperm quality begins to decline around 35 and worsens after 40,” explains Dr. Singh. Ageing men face reduced motility and higher DNA fragmentation, raising miscarriage and genetic risks.
Myth 2: Frequent ejaculation permanently reduces sperm count
Dr. Singh clarifies: “Sperm production never stops. While sperm count may be lower immediately after ejaculation, it bounces back quickly. In fact, regular ejaculation may improve sperm quality by expelling older sperm.”
Myth 3: Tight underwear causes infertility
While prolonged heat (hot tubs, saunas, heat waves) can lower sperm temporarily, everyday use of snug briefs does not cause infertility. “Loose boxers might help a little, but it’s heat exposure, not underwear style, that matters,” says Dr. Singh.
Myth 4: Alcohol and smoking don’t affect sperm
“This is false,” stresses Dr. Singh. Smoking damages DNA, lowers motility, and reduces sperm counts. Heavy drinking disrupts hormone levels and can impair sexual function. Moderate drinking may be safe, but excessive alcohol should be avoided when trying to conceive.
Myth 5: Stress has no impact on sperm
Psychological and physical stress lowers testosterone, causing reduced libido and even sexual dysfunction. Dr. Singh advises managing stress with exercise, meditation, proper sleep, or counselling.
What Really Affects Sperm Health
Lifestyle Habits: Diets rich in antioxidants, vitamins (C, D, E), and minerals (zinc, selenium) support sperm health. Obesity, poor nutrition, and inactivity damage sperm quality.
Medical Conditions: Varicocele (dilated scrotal veins), infections, endocrine imbalances, and chronic diseases like diabetes can disrupt sperm production.
Early Checkups: Couples trying for over a year without success should both be tested. “Semen analysis is simple, informative, and helps guide treatment,” notes Dr. Singh.
Key Takeaways
Infertility is not just a women’s health issue — men contribute to nearly half the cases worldwide. Knowing the real risk factors, busting myths, and seeking timely medical help can make all the difference. Treatments like IVF and ICSI offer hope, but the first step is awareness.
“By focusing on healthy lifestyle choices and separating facts from fiction, men can actively protect and improve their reproductive health,” Dr. Singh concludes.
Kirti Pandey is a senior independent journalist.
[Disclaimer: The information provided in the article, including treatment suggestions shared by doctors, is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.]
Check out below Health Tools-
Calculate The Age Through Age Calculator