{By: Dr Prateik Poddar}
Living with persistent digestive problems can be frightening, confusing and exhausting. Many patients walk into the clinic after months of unexplained diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss or blood in stools, wondering what exactly is happening inside their body. Two conditions often responsible for such symptoms are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Understanding these conditions early can transform outcomes, prevent complications and restore quality of life.
ALSO READ: Delhi’s Air Under Threat: Dangerous Superbugs Found At Alarming Levels In New Scientific Study
Crohn’s Disease vs Ulcerative Colitis: The Core Difference
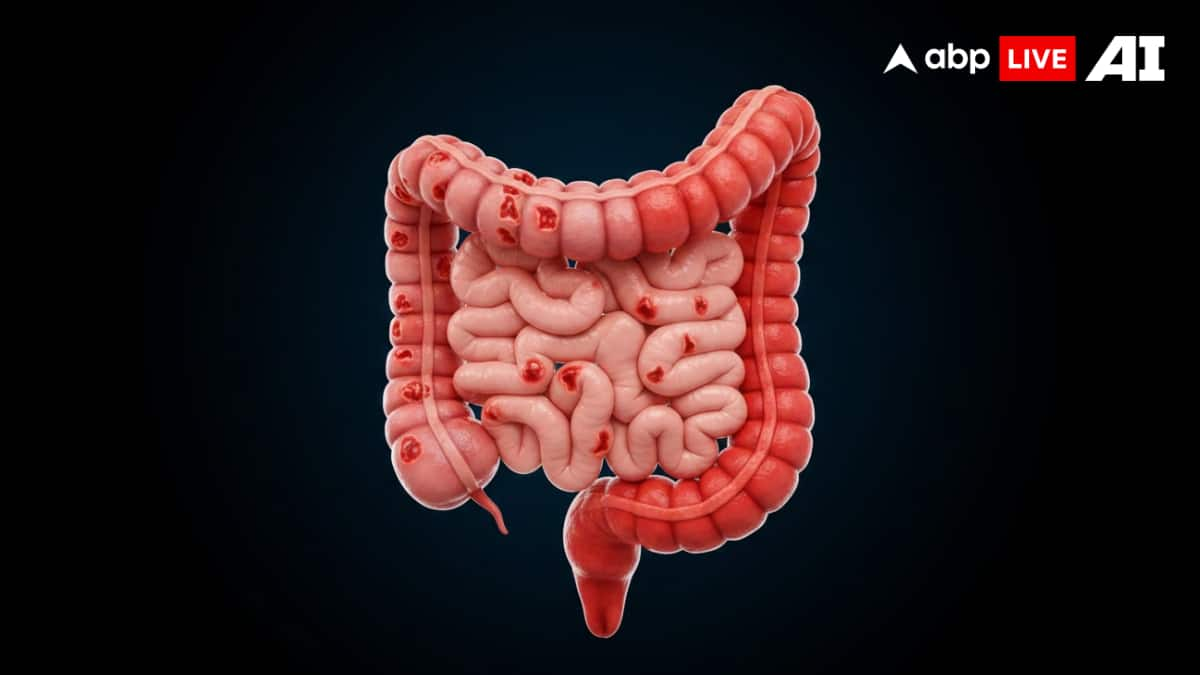
The fundamental difference lies in how and where the inflammation occurs.
Crohn’s disease causes inflammation through all layers of the intestinal wall and may affect any part of the digestive tract, from the stomach to the end of the intestine. The inflammation appears in a skip pattern, meaning diseased segments are interspersed with healthy sections.
Ulcerative colitis, in contrast, involves only the inner lining of the large intestine. The inflammation progresses in a continuous pattern, beginning at the rectum and extending backward through the colon to varying extents.
Which Parts Of The Gut Are Affected?
Crohn’s disease can involve any region of the gastrointestinal tract. Some patients even develop inflammation around the anal region, leading to painful discharge and fistulas.
Ulcerative colitis remains limited to the large intestine, always starting at the rectum and spreading upward in a predictable continuous manner.
Early Warning Signs And Common Symptoms

IBD often announces itself quietly before becoming aggressive. The most frequent symptoms include:
- Chronic diarrhea
- Blood in stools
- Persistent abdominal pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
Ignoring these signs allows silent inflammation to progress, increasing the risk of complications.
How Is IBD Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis relies on a stepwise evaluation using multiple tools:
- Detailed clinical assessment
- Colonoscopy for direct visualisation
- Blood tests and stool tests to assess inflammation and infection
- Imaging such as CT scans when required
- Early testing prevents long-term damage and improves treatment success.
Modern Treatment Approach

IBD is an autoimmune disorder, and treatment focuses on immune suppression to control inflammation. This includes:
- Steroids and advanced immunomodulatory medicines
- Long-term maintenance therapy to prevent flare-ups
- Nutritional support and symptom management
- Surgery, when medications alone are insufficient
Treatment plans are personalised, aiming not only for symptom control but also for deep healing of the intestinal lining.
Living Well With IBD
With timely diagnosis, correct therapy and regular follow-up, most patients lead full, productive lives. Awareness, early action and consistency in treatment are the strongest weapons against disease progression.
Your digestive system speaks to you every day. Learning to listen early can change everything.
Dr Prateik Poddar is a Consultant Gastroenterologist and Hepatologist, at ILS Hospitals.
[Disclaimer: The information provided in the article is shared by experts and is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.]
Check out below Health Tools-
Calculate The Age Through Age Calculator


